复旦大学教授,曾任上海期智研究院PI。
长期从事大气辐射与遥感研究,曾荣获德国“洪堡学者”和日本学术振兴会海外特别研究员两项国际人才项目、清华大学—浪潮集团计算地球科学青年人才奖(2019年、全国3人)、国际摄影测量与遥感协会大气环境遥感工作组授予的大气环境遥感与协同分析研讨会青年学者奖(2018年、全国1人)、上海市浦江(A类)人才计划(2020年)、江苏省“333人才工程”中青年科学技术带头人(2018年)、江苏省高校“青蓝工程”中青年学术带头人(2019年)。目前担任科技部重点研发课题组长,共主持3项国家自然科学基金,共计发表或录用SCI(E)论文59篇,其中第一/通讯作者SCI(E)论文39篇,ESI高被引论文1篇,获国家发明专利1项,论文成果受到国际顶级平流层辐射学家、英国皇家学会会士K.P. Shine教授及国际大气辐射学家、原国际辐射委员会主席Teruyuki Nakajima教授等人的广泛引用并给予正面评价。
个人荣誉
2018年,德国“洪堡学者”
2016年,日本学术振兴会海外特别研究员
2019年,第七届清华大学—浪潮集团计算地球科学青年人才奖
2018年,获国际摄影测量与遥感协会大气环境遥感工作组授予的大气环境遥感与协同分析研讨会青年学者奖
2018年,江苏省“333工程”中青年科学技术带头人
2019年,江苏省高校“青蓝工程”中青年学术带头人
大气辐射与卫星气象学
人工智能在大气科学中的应用
数值模式物理过程参数化
成果6:基于前向辐射传输模拟和机器学习的Himawari-8卫星沙尘气溶胶识别算法
沙尘是影响地气系统的重要因素,前人在沙尘识别的研究上通常关注严重沙尘暴事件,目前对弱的沙尘气溶胶识别研究较少。张峰团队通过敏感性分析实验,利用快速辐射传输模式ERTM对沙尘、水云和冰云的辐射特性进行模拟,发现引入了模拟的晴空亮温后能有效提高沙尘气溶胶和云的区分度。以CALIPSO卫星二级产品作为标签,用Himawari-8卫星观测数据、MODIS产品和ERA-5再分析资料与之匹配制作数据集并构建人工神经网络ANN模型(图2)用于晴空、云和沙尘的分类。结果表明,我们提出的沙尘气溶胶识别算法能有效的识别沙尘,精度达90%以上,召回率达84%以上。应用于区域沙尘识别时,对比欧洲气象中心的官方沙尘产品,我们的结果与CALIPSO更相近,在识别薄的沙尘气溶胶上具有优势(图3)。
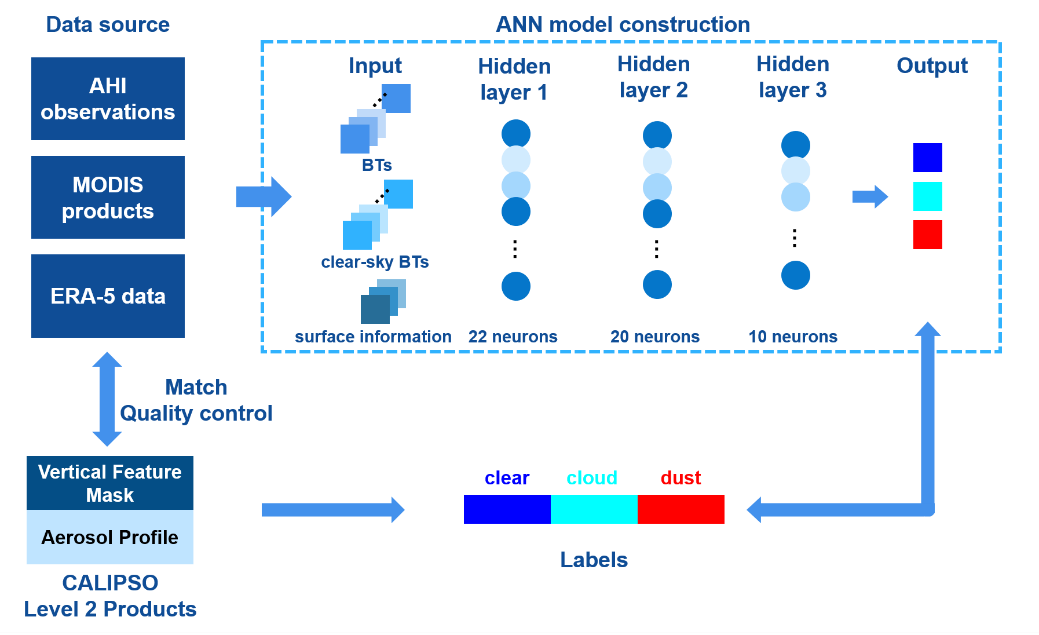
图. 数据集制作流程图及ANN模型结构
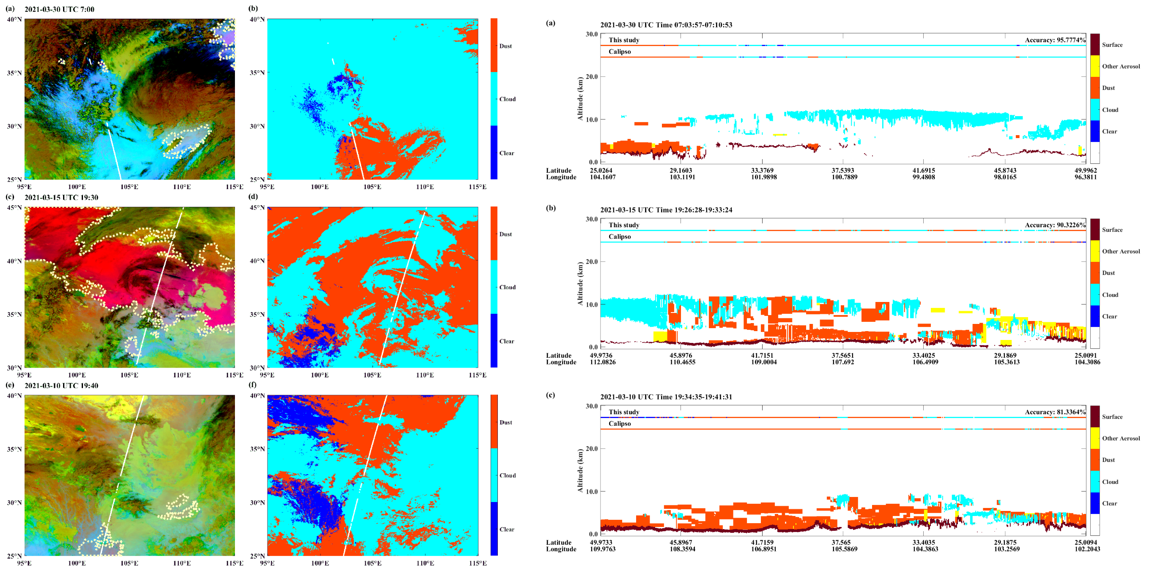
图. 沙尘气溶胶识别结果与CALIPSO观测、沙尘产品的对比
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
成果5:提出新的超分辨率框架重构30年全球细粒度夜间灯光观测
城市在夜晚发出的灯光能被卫星记录下来,被广泛用于城市范围制图、社会经济指数估算、人道主义冲突和自然灾害检测、能源消耗和碳排放估算等方面。提供夜光数据的主要卫星传感器是DMSP-OLS和NPP-VIIRS。DMSP-OLS采集了1992年至2019年的夜光数据,但是由于没有标定,它的数据在年份之间不能直接对比,并且图像十分模糊。NPP-VIIRS是更先进的传感器,采集了2012年至今的数据,它的数据在年份之间可以直接对比,图像也更清晰。以往的研究只局限于单个传感器,长时间与细粒度的夜光观测无法兼得。本研究力求整合两个传感器,首次实现1992年至今的长时间、细粒度的夜光观测,以促进从太空视角研究人类活动。
为了实现长时间序列的观测,张峰团队提出新的相互定标方法提升DMSP-OLS的连续性。重点是引入时空变异系数以选择更好的定标场。通过这种新的定标方法,显著提升了DMSP-OLS数据在年份之间的连续性,与前人方法相比,具有明显优势。为了实现细粒度的观测,张峰团队提出学习年际差异的超分辨率新框架,并据此设计了新的超分辨率模型DeepNTL,将DMSP-OLS重构为NPP-VIIRS数据,如图4所示。经过对一些特殊设施如道路、机场的调查,发现本研究的超分辨率结果能首次揭示这些设施最近30年的历史变迁。此外,通过统计检验,发现本研究的超分辨率结果在不同尺度与真实图像的一致性都明显高于其他方法。
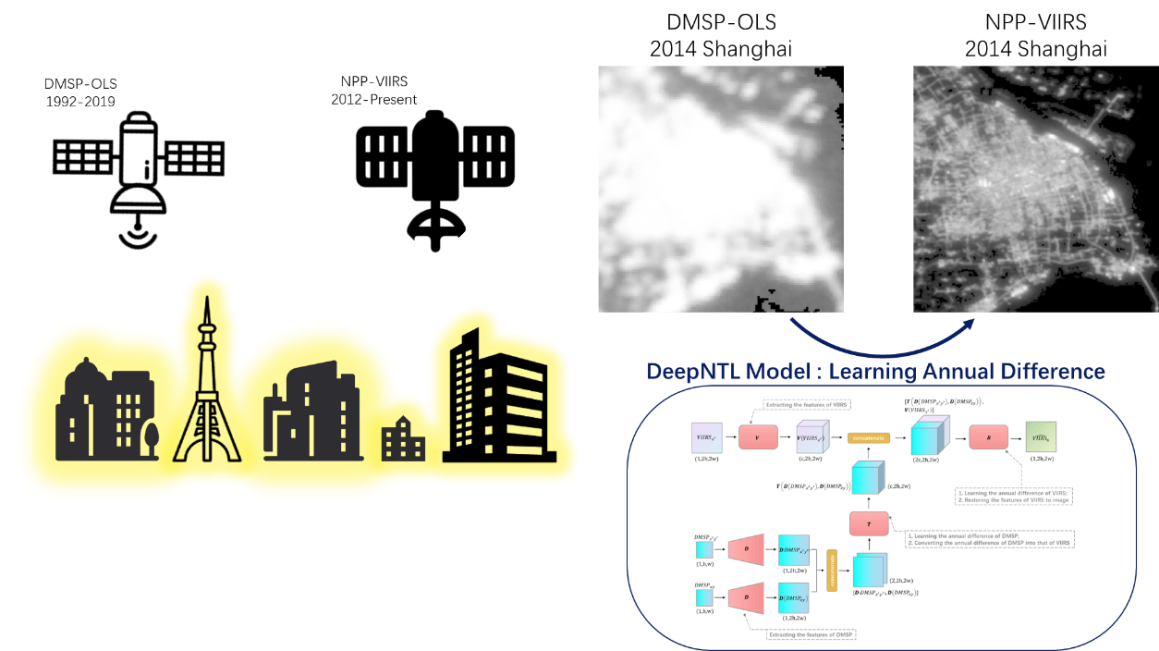
图. DeepNTL模型对夜间灯光数据进行30年的细粒度重构
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
成果4:矢量辐射传输算法
微波辐射传输模拟的准确度会直接影响卫星资料同化和定量遥感反演精度。张峰团队建立了平面平行大气下的红外微波矢量辐射传输方案POLDDA (Polarized Discrete ordinate adding Approximation)。采用离散纵标法求解包含多次散射项的单层微波矢量辐射传输方程;在离散纵标空间中同时处理I和Q分量(图5)。Chandrasekhar的不变性原理用于处理多层辐射传输过程,该累加过程对单层大气光学厚度没有限制。在不同的大气条件下,不同流数设置下,评估了POLDDA的计算精度和效率。结果表明,对于I和Q分量,POLDDA(使用32或16流)和标准值(32流RT3)之间的相对误差可以忽略不计。8流POLDDA的精度略有下降,但仍优于8流RT3。POLDDA计算效率远高于RT3,尤其是在光学厚度和流数(≥16流)较大的情况下。与RT3不同的是,POLDDA的计算耗时不会随着光学厚度的增加而增加(图6)。该成果于2022年在《Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer》杂志发表题为“Polarized discrete ordinate adding approximation for infrared and microwave radiative transfer”的论文。

图. 矢量微波辐射传输的不变性原理示意图
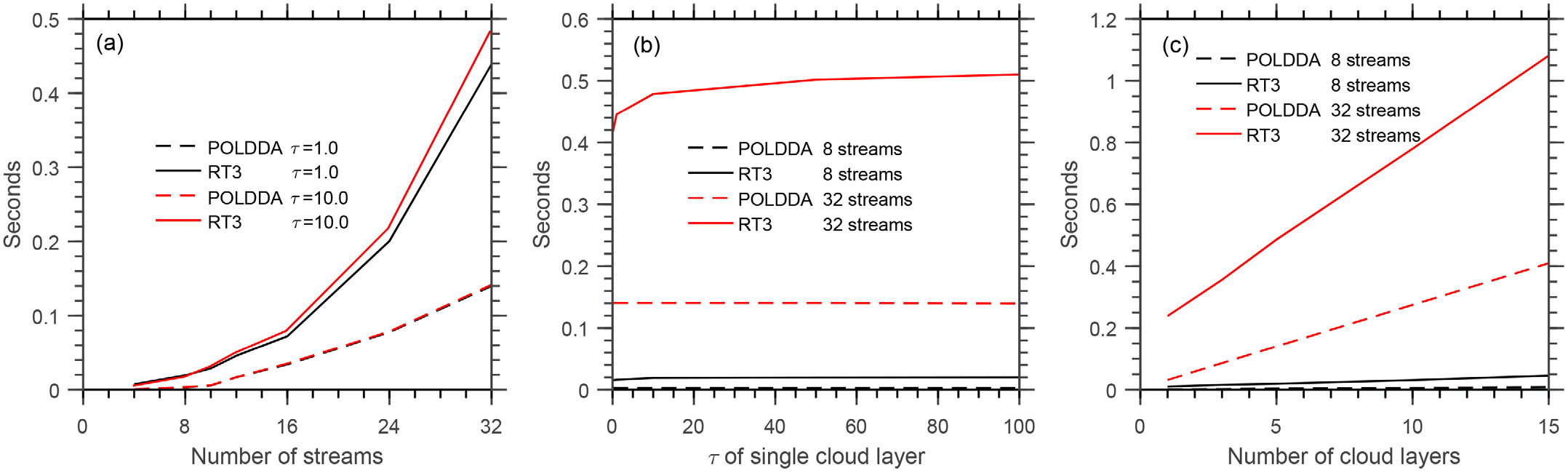 图. 计算时间(秒)与(a)流数、(b)云层光学厚度和(c)云层数的关系
图. 计算时间(秒)与(a)流数、(b)云层光学厚度和(c)云层数的关系
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
成果3:水云光学性质参数化方案
云的光学属性对计算有云大气的辐射传输至关重要,云辐射通过影响大气顶反射和到达地表的总辐射通量以及整层大气的加热/冷却率,从而影响大气稳定度、蒸发等过程,作用于大气动力过程。
张峰团队通过构建Back Propagation(BP)神经网络算法,拟合云有效粒子半径、云水路径和方差与带平均非对称因子、带平均单次散射反照率、带平均消光系数、带平均勒让德系数的非线性关系。该项研究的特色是在前人考虑云有效半径、云水路径的基础上,增加考虑了方差项,建立四层的神经网络对云光学性质进行参数化,在保证精度的同时极大简化了模式中的计算过程。利用米散射程序计算水云光学性质数据库作为真值,评估基于BP模型模拟的光学性质误差。各个光学参数的平均相对误差均小于1%,平均绝对误差均小于0.002。模拟的光学性质结果与MIE散射计算结果进行相关性分析,由图7可看出相关系数均大于0.999,模型拟合能力良好,后续可以将该模型接入气候模式中,加速辐射过程计算。
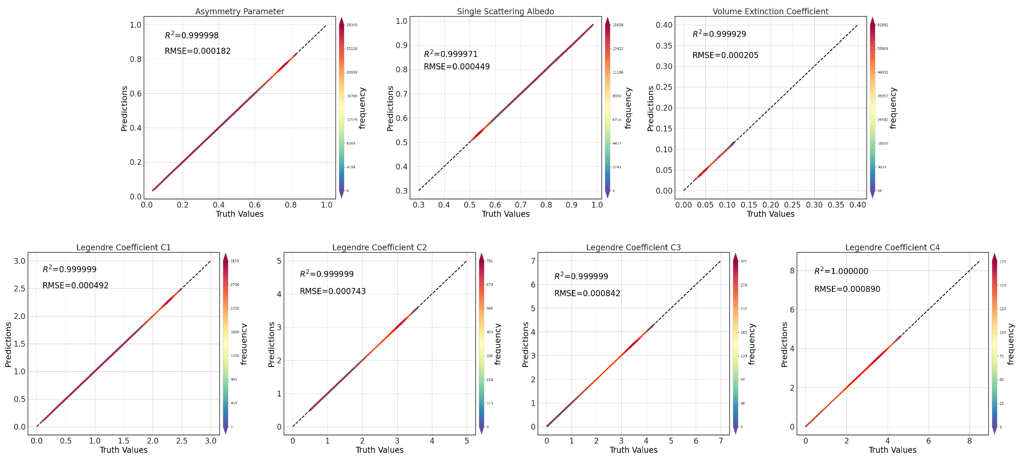
图. 水云光学性质模拟结果相关性分析图
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
成果2:OMCKD长波气体吸收参数化方案
张峰团队建立长波大气吸收模型,模拟大气透过率:基于Hitran2016气体吸收数据库,采用相关K分布方法构建长波(10-3250cm-1)宽带的气体吸收参数化方案——OMCKD方案。该项研究的特色是采用交替映射相关K分布方法,成功分离了同一波段中不同气体的强吸收波数,实现了宽带多气体联合透过率的高效、高精度计算。此外,该项研究通过最优估计方法,确定了各气体的等效吸收系数的修正参数,进一步提高了透过率模拟精度。如图8,在标准大气廓线情况下,OMCKD方案模拟的辐射通量误差不超过0.30 W m-2,加热率误差不超过0.11 K d-1。在工业革命前和二氧化碳加倍情景下,OMCKD模拟的晴空辐射通量和加热率精度均高于国际通用的快速辐射传输模式RRTMG。该成果已提交专利申请,专利申请号为022104772138。
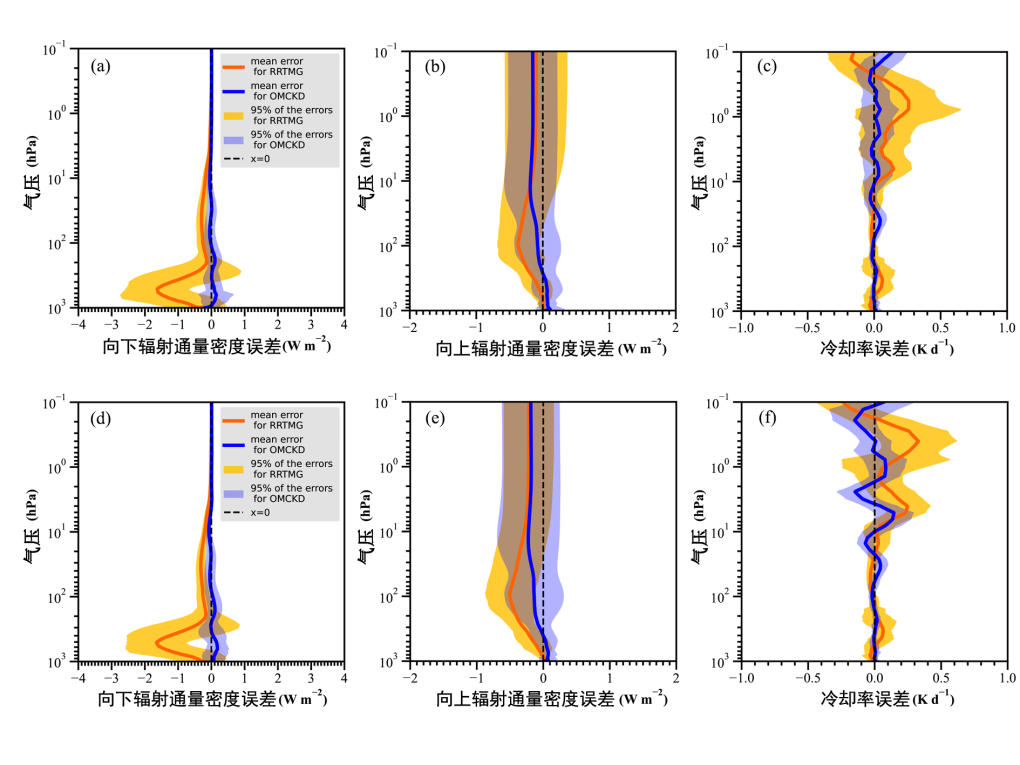
图. OMCKD方案和RRTMG方案的误差廓线。实线为50条廓线的平均误差,阴影区域为95%误差范围。蓝色为OMCKD,橘色为RRTMG。(a)(b)(c)为工业革命前情景下,向下辐射通量密度误差廓线,向上辐射通量密度误差廓线和冷却率误差廓线。(d)(e)(f)与(a)(b)(c)相同,但为二氧化碳加倍情景下。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
成果1:基于迁移学习的全天候云产品反演方法
云在影响大气动力、水汽循环和地球辐射平衡方面发挥着重要的作用。云参数的变化可以直接影响长波和短波的辐射传输,调节全球或局部能量的收支和大气中能量的垂直分布,从而影响全球和区域的气候。然而不同的观测方法对云的描述存在着差异,这影响着人们深入理解云与大气的相互作用过程。
张峰团队提出了一种基于迁移学习的全天候云产品反演方法,该方法使用静止轨道卫星观测的热红外通道亮温作为深度学习模型ResUnet的主要输入,分别以Himawari-8官方云产品和MODIS官方云产品作为标签进行预训练和迁移学习(图1),建立的模型仅需14秒即可对静止轨道卫星成像区域的云相态、云有效粒子半径、云光学厚度和云顶高度进行完整的反演。该方法使用深度学习模型建立输入特征与真实目标之间面到面的映射关系,可以充分地识别出云在空间上的特征与联系,弥补了厚云反演能力不足的缺陷。此外,该方法可以全天候的进行工作,得到的云产品不仅满足高频次、大范围的需求,且在精度上也明显优于静止轨道卫星官方云产品。团队已经将此方法应用于Himawari-8卫星和FengYun-4A卫星上,并且生产了两年的云产品,这些产品将被公开发布,以帮助人们更好地理解云和大气之间的相互作用。
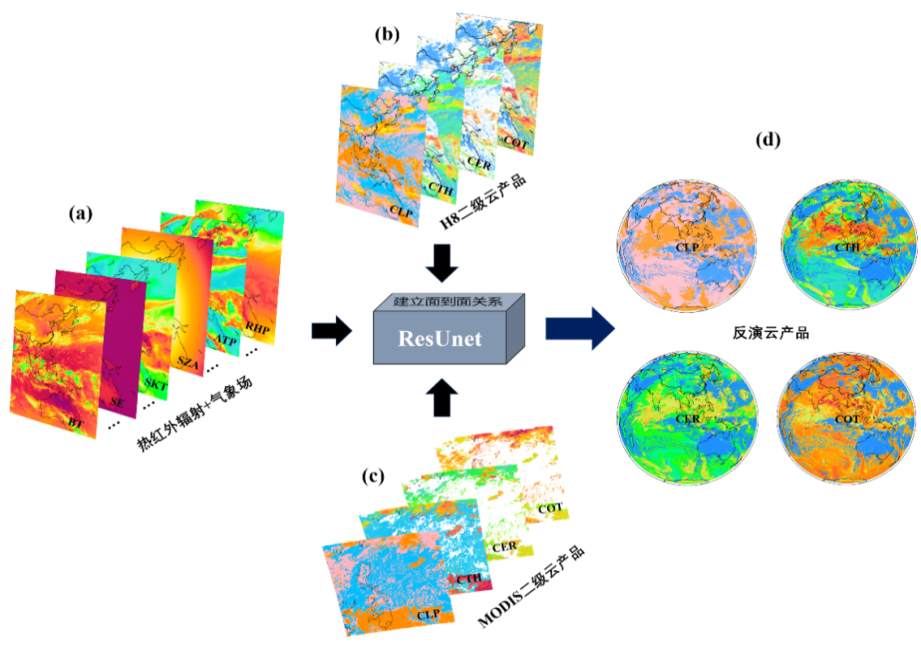
图. 基于迁移学习的全天候云产品反演流程图
58. Li W, Zhang F, Yu Y, et al., The semi-diurnal cycle of deep convective systems over Eastern China and its surrounding seas in summer based on an automatic tracking algorithm, Climate Dynamics 查看PDF
57. Zhang J, Liu P, Zhang F, et al., Ensemble meteorological cloud classification meets internet of dependable and controllable things, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(5): 3323-3330. 查看PDF
56. Zhang Q, Chen Y, Liu Y. , Study on the online detection of atmospheric sulfur via laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 36(5): 1028-1033. 查看PDF
55. Qu Y, Ji H, Oudray F, et al. , Online composition detection and cluster analysis of Tibetan incense, Optik, 241: 166999 查看PDF
54. Qiong Wu, Yi-Xuan Shou, Lei-Ming Ma, Qifeng Lu, Rui Wang, Estimation of Maximum Hail Diameters from FY-4A Satellite Data with a Machine Learning Method, Optical and Laser Remote Sensing of Atmospheric Composition 查看PDF
53. Xiao H, Zhang F, Shen Z, et al., Classification of weather phenomenon from images by using deep convolutional neural network, Earth and Space Science, 8(5): e2020EA001604 查看PDF
52. Gao S, Mao J, Zhang W, et al., Atmospheric moisture shapes increasing tropical cyclone precipitation in southern China over the past four decades, Environmental Research Letters, 16(3): 034004 查看PDF
51. Zhang Y, Wu K, Zhang J, et al., Estimating Rainfall with Multi-Resource Data over East Asia Based on Machine Learning, Remote Sensing, 13(16): 3332 查看PDF
50. Liang Xiangsan, Fen Xu, Yineng Rong, Renhe Zhang, Xu Tang, Feng Zhang, El Niño Modoki can be mostly predicted more than 10 years ahead of time, Scientific Reports 查看PDF
49. X. San Liang*, An overview of the quantitative causality analysis and causal graph reconstruction based on a rigorous formalism of information flow, 20th International Conference of the Italian Association for Artificial Intelligence 查看PDF
48. X. San Liang*, Measuring the importance of individual units in producing the collective behavior of a complex network, Chaos 查看PDF
47. X. San Liang*, Normalized Multivariate Time Series Causality Analysis and Causal Graph Reconstruction, Entropy 查看PDF
46. Lei Wang and Mingfang Ting, Stratosphere-Troposphere Coupling Leading to Extended Seasonal Predictability of Summer North Atlantic Oscillation and Boreal Climate, Geophysical Research Letters 查看PDF
45. Runzi Chen, Guokun Dai, Ran Liu, and Lei Wang, Seasonal Influence of the Atmosphere and Ocean on the Fall Sea Ice Extent in the Barents-Kara Seas, Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 查看PDF
44. Lingyun Meng, Jane Liu*, David W. Tarasick, William J. Randel*, Andrea K.Steiner, Hallgeir Wilhelmsen, Lei Wang, Leopold Haimberger, Continuous rise ofthe tropopause in theNorthern Hemisphere over 1980–2020, SCIENCE ADVANCES:RESEARCH ARTICLE 查看PDF
43. Xulong He, Ruonan Zhang*, Shuoyi Ding and Zhiyan Zuo, Interdecadal Linkage Between the Winter Northern Hemisphere Climate and Arctic Sea Ice of Diverse Location and Seasonality, Frontiers in Earth Science 查看PDF
42. Changlin Chen∗, Guihua Wang, Yunwei Yan and Fengyun Luo, Projected sea level rise on the continental shelves of the China Seas and the dominance of mass contribution, Environmental Research Letters 查看PDF
41. Haixia Xiao, Feng Zhang, Zhongping Shen, Kun Wu, and Jinglin Zhang, Classification of Weather Phenomenon From Images by Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network, Earth and Space Science 查看PDF
40. Wenwen Li, Feng Zhang*, Fengzi Bao , Kun Wu, Jiangnan Li , Peng Zhang, Wei Han, Polarized discrete ordinate adding approximation for infrared and microwave radiative transfer, Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer 查看PDF
39. Shi Yi-Ning, Wenwen Li, Kun Wu*, Feng Zhang, Qi Chen, A broadband infrared radiative transfer scheme including the effect related to vertically inhomogeneous microphysical properties inside water clouds, Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer 查看PDF
38. Cui Qian, Zhang Feng, Fu Shaoyun ,Wei Xiaoli*, Ma Yue and Wu Kun, High Spatiotemporal Resolution PM2.5 Concentration Estimation with Machine Learning Algorithm: A Case Study for Wildfire in California, Remote Sensing 查看PDF
37. Lin Han, Zhenglong Li, Jun Li, Feng Zhang, Min Min, W. Paul Menzel, Estimate of daytime single-layer cloud base height from Advanced Baseline Imager measurements, Remote Sensing of Environment 查看PDF
36. Wenwen Li, Feng Zhang*, Han Lin, Xiaoran Chen, Jun Li, and Wei Han, Cloud detection and classification algorithms for Himawari-8 imager measurements based on deep learning, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 查看PDF
35. Zhang, Zhuang, X. San Liang*,, Multiscale interactive processes underlying the heavy rainstorm associated with a landfalling atmospheric river, Atmosphere 查看PDF
34. Liang, X. San*,, The causal interaction between complex subsystems, Entropy 查看PDF
33. Zhang, Yinchen, X. San Liang*, The causal role of South China Sea on the Pacific-North American teleconnection pattern, Climate Dynamics 查看PDF
32. B. Sun*, C. Gao, D. Liang, Z. Liu, and J. Liu, Capability and convergence of linearized invariant-imbedding T-matrix and physical-geometric optics methods for light scattering, Opt. Express 查看PDF
31. Chenxu Gao, Dongbin Liang, Bingqiang Sun*, Jian Liu and Zhaoyuan Liu, Linearized Single-Scattering Property Database for Hexagonal Prism Ice Particles, Remote Sensing 查看PDF
30. YuRui Li, Yang Zhang , YiJun Zhang, and Paul R. Krehbiel, Analysis of the Configuration Relationship Between the Morphological Characteristics of Lightning Channels and the Charge Structure Based on the Localization of VHF Radiation Sources, Geophysical Research Letters 查看PDF
29. Wenjuan Zhang , Yijun Zhang*, Shoujuan Shu , Dong Zheng and Liangtao Xu, Lightning Distribution in Tropical Cyclones Making Landfall in China, Frontiers in Earth Science 查看PDF
28. Chen, G., and W. Wang, Short‐term precipitation prediction for contiguous United States using deep learning, Geophysical Research Letters 查看PDF
27. Rui Lyu, Wei Gao , Yarong Peng , Yijie Qian , Qianshan He, Tiantao Cheng*, Xingna Yu and Gang Zhao* , Fog–Haze Transition and Drivers in the Coastal Region of the Yangtze River Delta, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 查看PDF
26. Xinyao Tan, Bingqiang Sun∗, Guochen Wang, Tiantao Cheng,∗ , Kan Huang, Fang Shen, Consecutive retrieval of aerosol optical depth and total suspended solid concentration in turbid coastal water of Eastern China, Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer 查看PDF
25. Jiuwei Zhao, Ruifen Zhan , Yuqing Wang, Leishan Jiang, and Xin Huang, A Multiscale-Model-Based Near-Term Prediction of Tropical Cyclone Genesis Frequency in the Northern Hemisphere, Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 查看PDF
24. Junyi Wang, Aifang Gao * , Shaorong Li , Yuehua Liu , Weifeng Zhao , Peng Wang ∗, Hongliang Zhang, Regional joint PM2.5-O3 control policy benefits further air quality improvement and human health protection in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and its surrounding areas, Journal of Environmental Science 查看PDF
23. Hai-Xia Xiao, Xi Liu, Rong Yu, Bin Yao, Feng Zhang, Ya-Qiang Wang, Contributions of internal climate variability in driving global and ocean temperature variations using multi-layer perceptron neural network, Advances in Climate Change Research 查看PDF
22. Wang F., R. Huang, L. Wang, Response of Tropical Convection over the Western Pacific to Stratospheric Polar Vortex during Boreal Winter, International Journal of Climatology 查看PDF
21. Shuiju Long,Xiaoli Wei,et al, Estimating daily ground-level NO2 concentrations over China based on TROPOMI observations and machine learning approach, Atmospheric Environment
20. Xuan Tong, Jingwei Li, Feng Zhang, et al., The deep-learning-based fast efficient nighttime retrieval of thermodynamic phase from Himawari-8 AHI measurements, Geophysical Research Letters 查看PDF
19. Zhao Z, Zhang F, Wu Q, et al., Cloud Identification and Properties Retrieval of the Fengyun-4A Satellite Using a ResUnet Model, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 61: 1-18. 查看PDF
18. Yumeng Li, Ruifen Zhan, Jiuwei Zhao, What caused the salient difference in rapid intensification magnitudes of Northwest Pacific tropical cyclones between 1998 and 2010?, Atmospheric Research 查看PDF
17. Zheng-Hang Fu, Ruifen Zhan, Jiuwei Zhao, Yohei Yamada, & Kexin Song, Future Projections of Multiple Tropical Cyclone Events in the Northern Hemisphere in the CMIP6-HighResMIP Models, Geophysical Research Letters
16. Qing Zhu, Yang Yu, Haixing Gong, Yanyu Wang, Hongli Wang, Weijie Wang, Bo Xu*, Tiantao Cheng*, Spatio-temporal characteristics of particles and ozone synergic pollutions and influence factors in the Yangtze River Delta, Frontiers in Environmental Science 查看PDF
15. Haixing Gong, Yanyu Wang, Guoyin Wang*, Yuqiu Gao, Guo Li, Zexing Kuang, Xianwang Zhuo, Jianrong Bi, Weijie Wang, Tiantao Cheng*, Quantifying the spatial representativeness of carbon flux footprints of a grassland ecosystem in the semi-arid region, Journal of Geophysical Research - Atmosphere 查看PDF
14. Yijie Qian, Dongmei Cai *, Miaomiao Zhang, Juntao Huo, Yusen Duan, Tiantao Cheng, Chemical composition, sources and secondary processes of aerosols in a megacity of China, Frontiers in Environmental Science 查看PDF
13. Guoxing Chen , Wei-Chyung Wang, Shixi Yang, Yixin Wang, Feng Zhang, and Kun Wu, A neural network‐based scale‐adaptive cloud‐fraction scheme for GCMs, Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 查看PDF
12. 肖海霞,张峰,王亚强,唐飞,郑玉, 基于生成对抗网络和卫星数据的云图临近预报, 应用气象学报 查看PDF
11. Xuan MA, Lei WANG, The Role of Ozone Depletion in the Lack of Cooling in the Antarctic Upper Stratosphere during Austral Winter, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences 查看PDF
10. Jiaqi Jin, Feng Zhang, Wenwen Li, Qiong Wu, Linlu Mei, and Lin Chen, A hybrid algorithm for dust aerosol detection: Integrating forward radiative transfer simulations and machine learning, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing
9. Jun Li, Feng Zhang, Jia Liu, Wenwen Li, Kun Wu, Shuai Hu, Han Lin, Parameterization of optical properties for liquid cloud droplets containing black carbon based on neural network, Optics Express
8. Xulong He, Ruonan Zhang*, Shuoyi Ding, Qinglong You, and Ziyi Cai, Decadal Changes in the Linkage Between Autumn Sea Ice and the Winter Eurasian Temperature in the 20th Century, Geophysical Research Letters
7. Ziyi Cai, Qinglong You*, Hans W. Chen, Ruonan Zhang*, Interdecadal variability of the warm Arctic-cold Eurasia pattern linked to the Barents oscillation, Atmospheric Research
6. Jingwei Li, Feng Zhang, Wenwen Li, Xuan Tong, BaoXiang Pan, Jun Li, Han Lin, Husi Letu, Farhan Mustafa, Transfer-learing-based approach to retrieve cloud properties using diverse remote sensing datasets, IEEE Transactions of Geoscience and Remote Sensing
5. W. Li, F. Zhang, C. Lu, J. Jin, Y.-N. Shi, Y. Cai, S. Hu, and W. Han, Integrated efficient radiative transfer model named Dayu for simulating the imager measurements in cloudy atmospheres, Optics Express
4. Yue Cai, Feng Zhang, Han Lin, Jiangnan Li, Hua Zhang, Wenwen Li, and Shuai Hu, Optimized Alternate Mapping Correlated K-Distribution Method for Atmospheric Longwave Radiative Transfer, Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems
3. Fuchang Wang, Xiaobiao Xu, Feng Zhang, and Leiming Ma, Structure of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation in Three Generations of Climate Models, Earth and Space Science
2. Jingjing Wang, Tan Tu, Feng Zhang, Fengjiao Shen, Jian Xu, Zhensong Cao, Xiaoming Gao, Stéphane Plus, and Weidong Chen, External-cavity diode laser-based near-infrared broadband laser heterodyne radiometer for remote sensing of atmospheric CO2, Optics Express
1. Xiaoli Wei, Qian Cui et al., Global aerosol typing classification using a new hybrid algorithm utilizing Aerosol Robotic Network data, Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics