2024-07-24
Recently, the team of Jianyu Chen from the Institute for Interdisciplinary Information Sciences at Tsinghua University and PI at Shanghai Qi Zhi Institute, in collaboration with Robotera completed the paper titled "Advancing Humanoid Locomotion: Mastering Challenging Terrains with Denoising World Model Learning(DWL)," which has been shortlisted for the prestigious Outstanding Paper Award at the Robotics: Science and Systems Conference 2024, one of the most difficult top conferences in the field of robotics (with only three papers selected). The conference took place from July 15th to 19th, 2024, at the Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands, and the proportion of papers receiving this honor is less than 1% of the total submissions.

Awards Ceremony Venue
The modern environmental design is centered on human needs and capabilities, and humanoid robots show significant advantages in mobility due to their human-like skeletal structure. Traditional gait control technologies such as Zero Moment Point (ZMP), Model Predictive Control (MPC), and Whole-Body Control (WBC) have made progress, but they are limited by the precise modeling of environmental dynamics. In contrast, Reinforcement Learning (RL) requires less modeling of the environment, and recent progress in model-free RL has demonstrated the potential to create universal leg motion controllers, enabling robots to learn from and adapt to diverse environments, often outperforming traditional model-based control methods.
To address the challenges of humanoid robot control, Chen Jianyu's team proposed the Denoising World Model Learning (DWL) technology to optimize the robot's capabilities in complex terrains. DWL has been verified on the Xiaoxing (XBot-S) and Xiaoxing Max (XBot-L), achieving the world's first end-to-end RL and zero-shot simulation-to-reality transfer, enabling the robot to walk stably on terrains including snow slopes, stairs, and resist external disturbances. The success of DWL is attributed to its innovative representation learning framework, which narrows the gap between simulation and reality through denoising, and it has also proposed a control method for the active 2-DOF ankle joint (closed-loop motion chain ankle mechanism), significantly enhancing the robot's robustness.
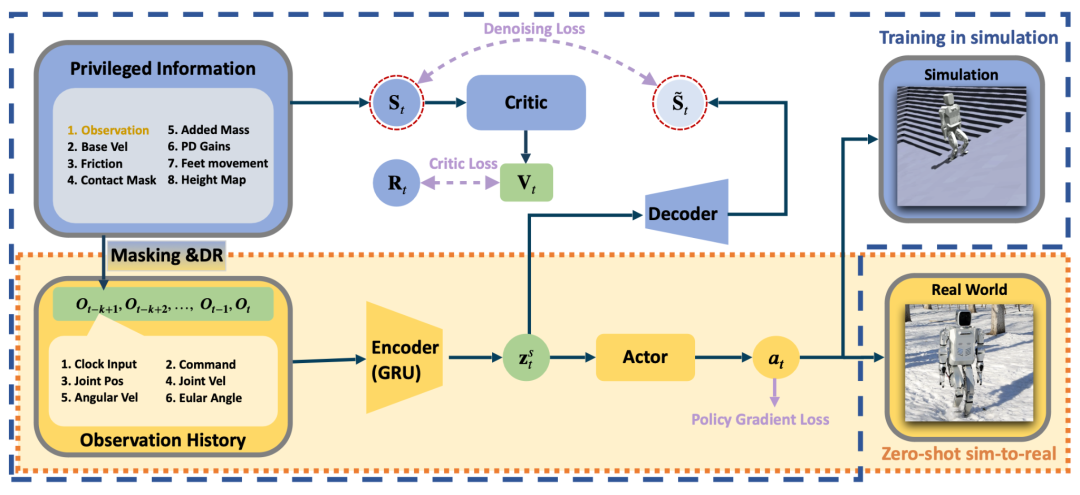
The DWL Algorithm Process
This work was collaboratively completed by Chen Jianyu's team and Xingdong Jiyuan. The co-first authors of this paper are Xinyang Gu, an engineer at Robotera, Yanren Wang, an intern at the Shanghai Qi Zhi Institute and a master's student at Tsinghua University, Xiang Zhu, a doctoral student at the same university, and Chengming Shi, a doctoral student at Tsinghua University.
Link to the Paper:https://roboticsconference.org/program/papers/58/